In the realm of survival and preparedness, the confluence of meticulous planning, adept skill acquisition, and strategic supply aggregation forms the bedrock of self-sufficiency. This trinity of preparedness – skills, supplies, and plans – is not merely a reactionary measure to unforeseen calamities but a proactive blueprint for resilience.

The journey towards this autonomy is punctuated by the acquisition of diverse skills – from basic first aid to advanced survival techniques – ensuring adaptability across various emergency scenarios.
Collecting the right medical supplies, tailored to meet specific health needs and potential risks, is a key step in building a solid defense against emergencies. This combination of a well-stocked medical kit and the necessary skills to use it, supported by thorough planning, makes the concept of medical preparedness practical and real. It equips individuals and families with the tools and knowledge to confidently face the uncertainties of emergencies, whether they’re natural or man-made.

Grab the PDF Download on Patreon
LIST: Essential Supplies for 15 Common Medical Emergencies
Check out: Elevate Your Preparedness: Building a High-Quality Personal Medical Kit
- Cuts, Scrapes, and Lacerations
- Bandages, antiseptic wipes, gauze, adhesive tape, butterfly closures, antibiotic ointment.
- Broken Bones and Sprains
- Splints, elastic bandages, triangular bandages, pain relievers.
- Burns
- Burn gel, sterile dressings, non-adherent dressings.
- Hypothermia and Frostbite
- Thermal blankets, hand warmers.
- Heat Exhaustion, Heat Stroke, Dehydration
- Electrolyte packets, cooling towels, water purification tablets.
- Insect Bites and Stings
- Antihistamines, hydrocortisone cream, EpiPen.
- Poisonous Plant Exposures
- Calamine lotion, hydrocortisone cream, antihistamines.
- Infections and Sepsis
- Antibiotics, antiseptic wipes, sterile dressings.
- Gastrointestinal Issues (Diarrhea, Vomiting)
- Anti-diarrheal medication, oral rehydration salts, anti-nausea medication.
- Respiratory Issues (Asthma, Pneumonia)
- Inhalers, cough suppressants, fever reducers.
- Cardiac Issues (Heart Attack)
- Aspirin, nitroglycerin, CPR mouth barrier.
- Eye Injuries
- Sterile eye wash, eye pads, bandages.
- Dental Emergencies
- Dental repair kit, pain relievers, gauze.
- Allergic Reactions
- Antihistamines, EpiPen, corticosteroids.
- Hypoglycemia or Diabetic Emergencies
- Glucose tablets, sugary snacks, insulin (for diabetics).
Cuts, Scrapes, and Lacerations
Cuts, scrapes, and lacerations are frequent injuries that can range from superficial grazes to deep incisions, necessitating prompt care to avert infection and aid in recovery.
Bandages
Bandages are vital for shielding wounds against contamination. They aid in stemming bleeding and facilitate the healing process. Select an appropriate size for effective coverage and replace the bandage periodically to ensure hygiene.
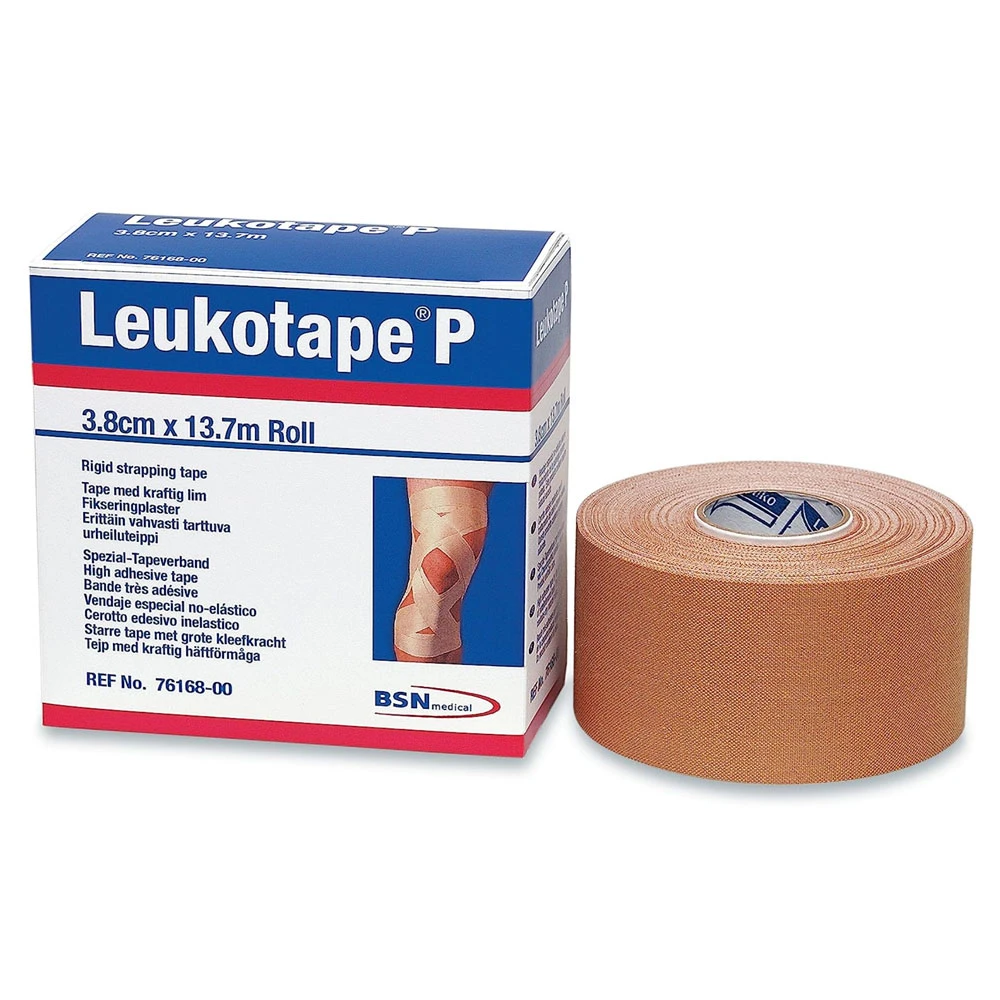
Leukotape P is also a great option for bandaging a wound.
Antiseptic Wipes
Antiseptic wipes are employed for cleansing wounds, eliminating germs and debris to thwart infection. Gently purify the area surrounding the injury with a wipe before applying further treatments. These are indispensable for initial wound management, particularly when soap and water are inaccessible.
Gauze
Gauze pads absorb blood and other fluids from wounds. They offer a protective layer, maintaining cleanliness. Use gauze in conjunction with adhesive tape to keep it in place, especially for more extensive or exposed wounds.
Adhesive Tape
Adhesive tape secures gauze and bandages. It should adhere firmly yet be gentle on the skin. Opt for hypoallergenic tape to minimize skin irritation risks.
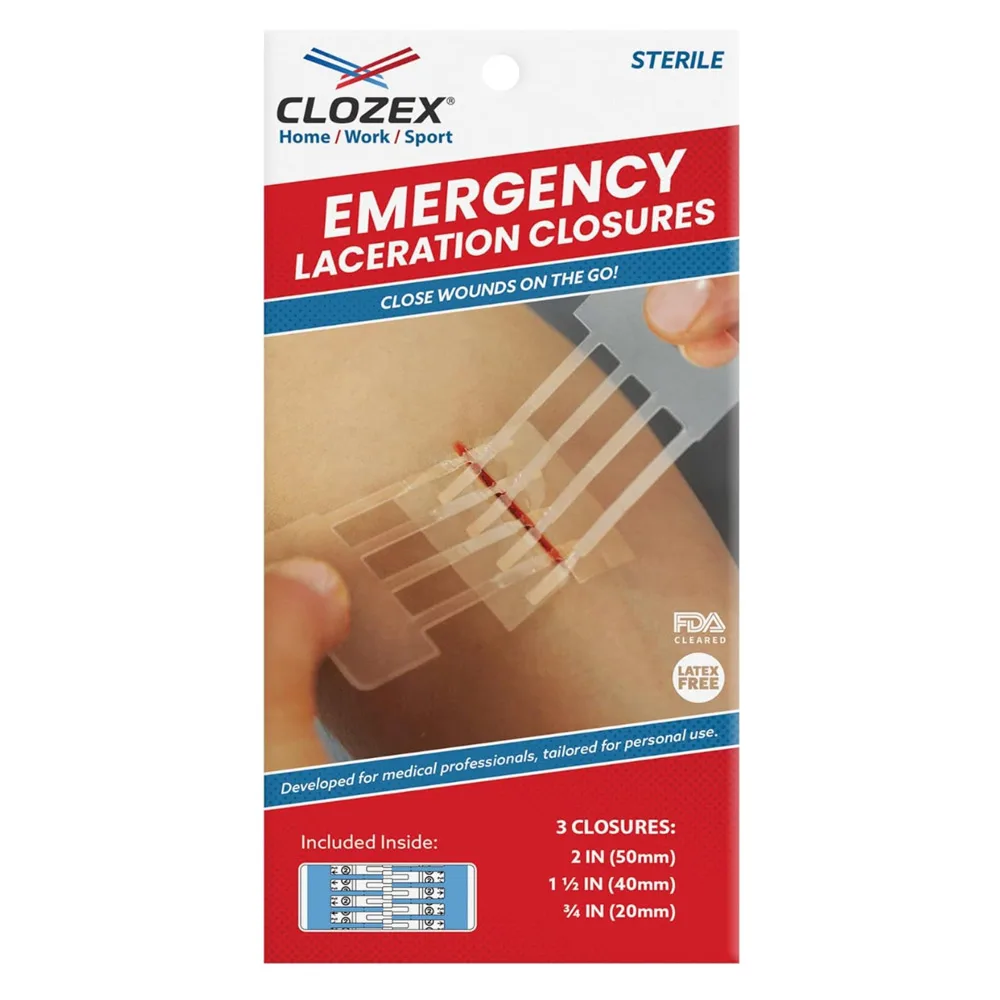
Butterfly Closures
Butterfly closures are utilized for suturing minor cuts or lacerations. They draw the skin on either side of the wound together, aiding in healing and minimizing scarring. These are optimal for injuries that are too significant for a bandage but not severe enough for stitches.
Antibiotic Ointment
Antibiotic ointment is applied to wounds to deter infection. It eradicates bacteria and maintains moisture in the wound, potentially accelerating healing. Administer a modest quantity on the wound before bandaging.
Broken Bones and Sprains
Broken bones and sprains are serious injuries that can result from accidents or falls. They often require immobilization and pain management to aid in healing and prevent further injury.
Splints
Splints are essential for immobilizing broken bones or sprains. They provide support and stability to the injured area, helping to maintain proper alignment and reduce movement. Splints come in various sizes and materials and should be applied carefully to avoid additional injury.
Elastic Bandages
Elastic bandages are used to compress and support sprained or injured limbs. They help reduce swelling and provide stability to the affected area. When applying an elastic bandage, ensure it’s snug but not too tight to avoid cutting off circulation.
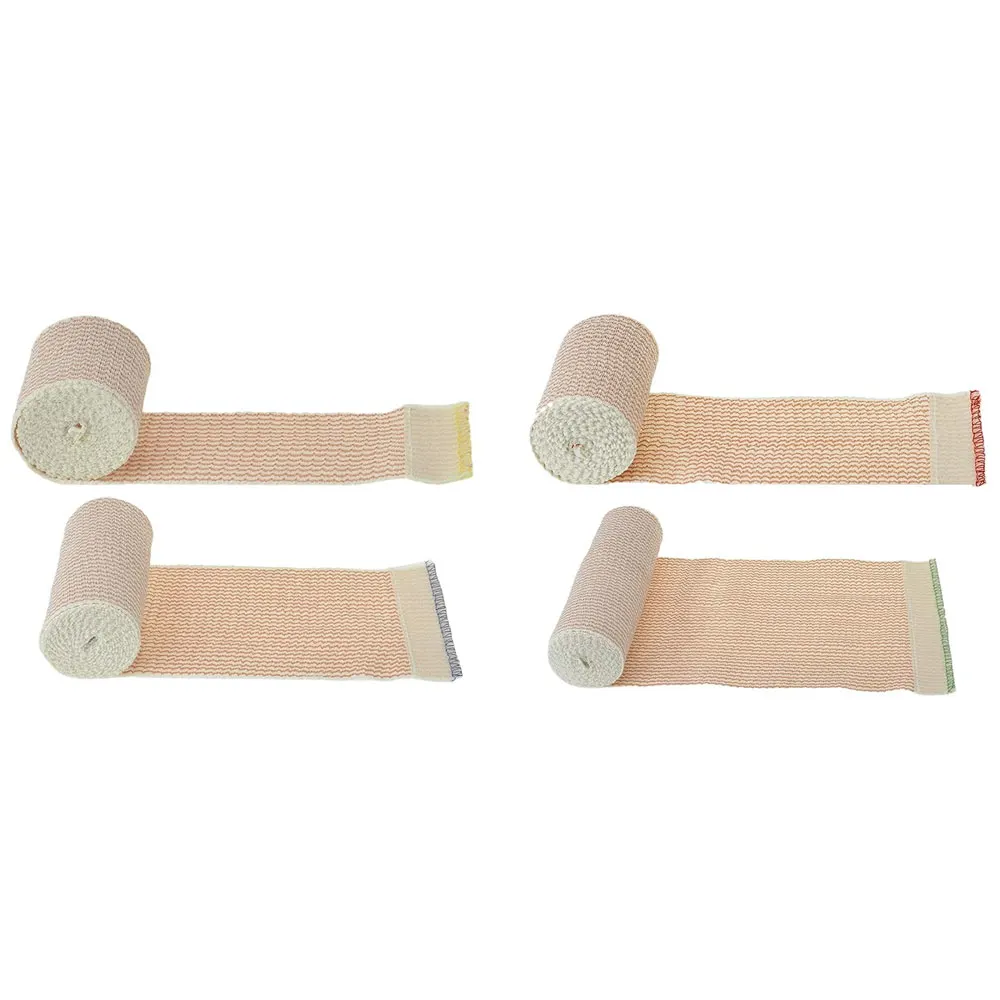
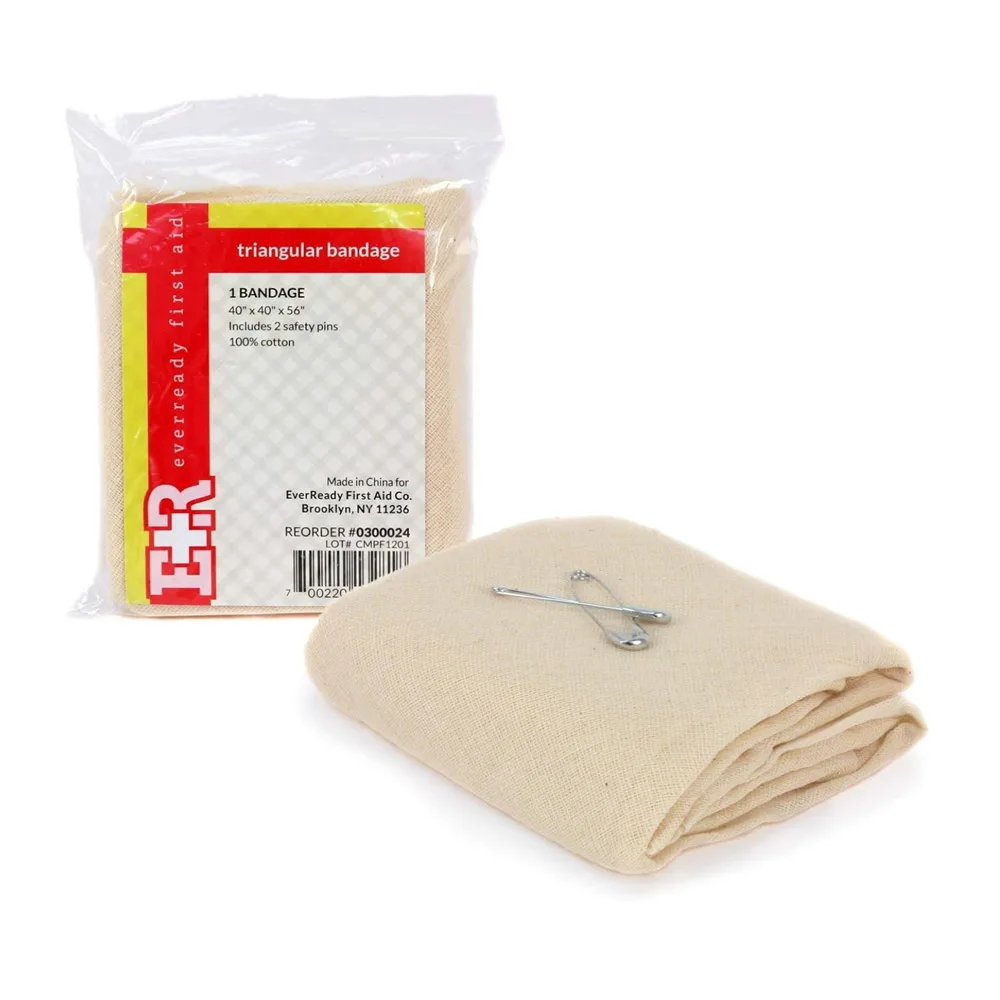
Triangular Bandages
Triangular bandages are versatile and can be used as slings, wraps, or to secure splints. They are particularly useful for shoulder, arm, or collarbone injuries. The bandage can be folded in various ways to suit the specific injury, providing support and reducing movement.
Pain Relievers
Pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, are important for managing pain associated with broken bones and sprains. They help in reducing inflammation and providing comfort to the patient. Always follow the recommended dosage and consider any allergies or medical conditions before administering pain relievers.
Burns
Burns, whether caused by heat, chemicals, electricity, or sun exposure, can range from mild to severe and require immediate attention. Proper treatment is key to reduce pain, prevent infection, and promote healing.
Burn Gel
Burn gel is specifically formulated to provide immediate relief from the pain of burns. It often contains ingredients like aloe vera or lidocaine, which soothe the skin and help reduce inflammation. Apply the gel gently to the affected area, being careful not to rupture any blisters that may have formed.
Sterile Dressings
Sterile dressings are crucial for covering and protecting burn wounds. They help maintain a clean environment around the burn, reducing the risk of infection. Choose dressings that are large enough to cover the entire burn area without sticking to the wound.
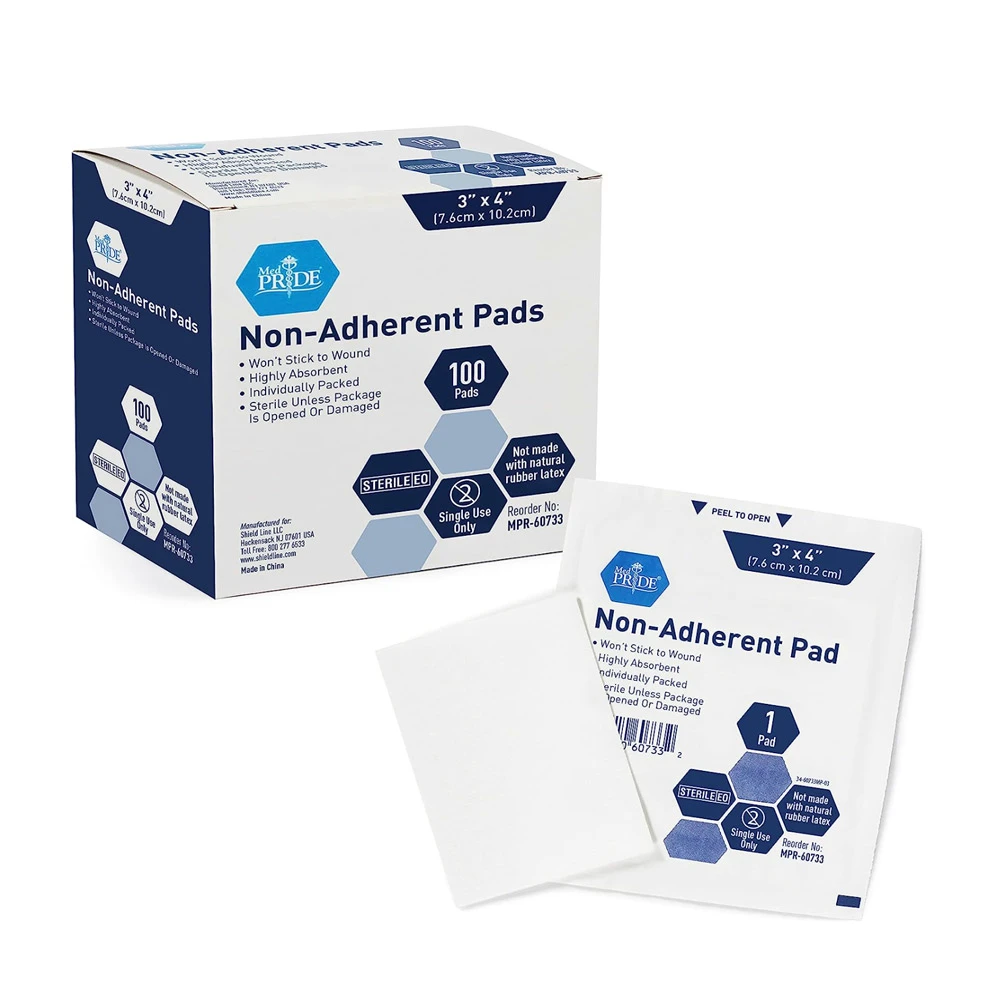
Non-Adherent Dressings
Non-adherent dressings are designed to cover the burn without sticking to the wound, making dressing changes less painful and reducing the risk of damaging newly formed tissue. These dressings are particularly useful for more severe burns where the skin is very tender and prone to damage.
Hypothermia and Frostbite
Hypothermia and frostbite are serious conditions caused by extreme cold exposure. Hypothermia occurs when body temperature drops below normal, while frostbite is the freezing of skin and other tissues. Immediate and appropriate response is important to prevent long-term damage or life-threatening situations.
Thermal Blankets
Thermal blankets, also known as space blankets, are essential in treating hypothermia. They are designed to retain body heat, helping to raise and stabilize the body’s core temperature. These blankets are lightweight, compact, and reflective, making them ideal for emergency situations. In cases of hypothermia, wrap the individual in a thermal blanket to conserve body heat and seek medical attention as soon as possible.
Hand Warmers
Hand warmers provide concentrated warmth and are particularly useful in cases of frostbite, which commonly affects the extremities like fingers and toes. They generate heat through a chemical reaction and can be placed in gloves or pockets to maintain warmth in the hands. When using hand warmers for frostbite, it’s important to gently warm the affected areas and avoid direct contact with the skin to prevent burns.
Heat Exhaustion, Heat Stroke, Dehydration
Heat exhaustion, heat stroke, and dehydration are serious conditions that occur due to excessive heat and insufficient hydration. They can have severe consequences if not promptly addressed, with symptoms ranging from fatigue and dizziness to life-threatening heat stroke.
Electrolytes
Electrolytes are VERY IMPORTANT in treating dehydration and heat-related illnesses. They help replenish essential minerals like sodium, potassium, and magnesium, which are lost through sweat. Electrolyte powder can quickly restore the body’s electrolyte balance, aiding in recovery from symptoms like muscle cramps and fatigue. They are especially important in severe cases of dehydration to maintain vital organ functions.
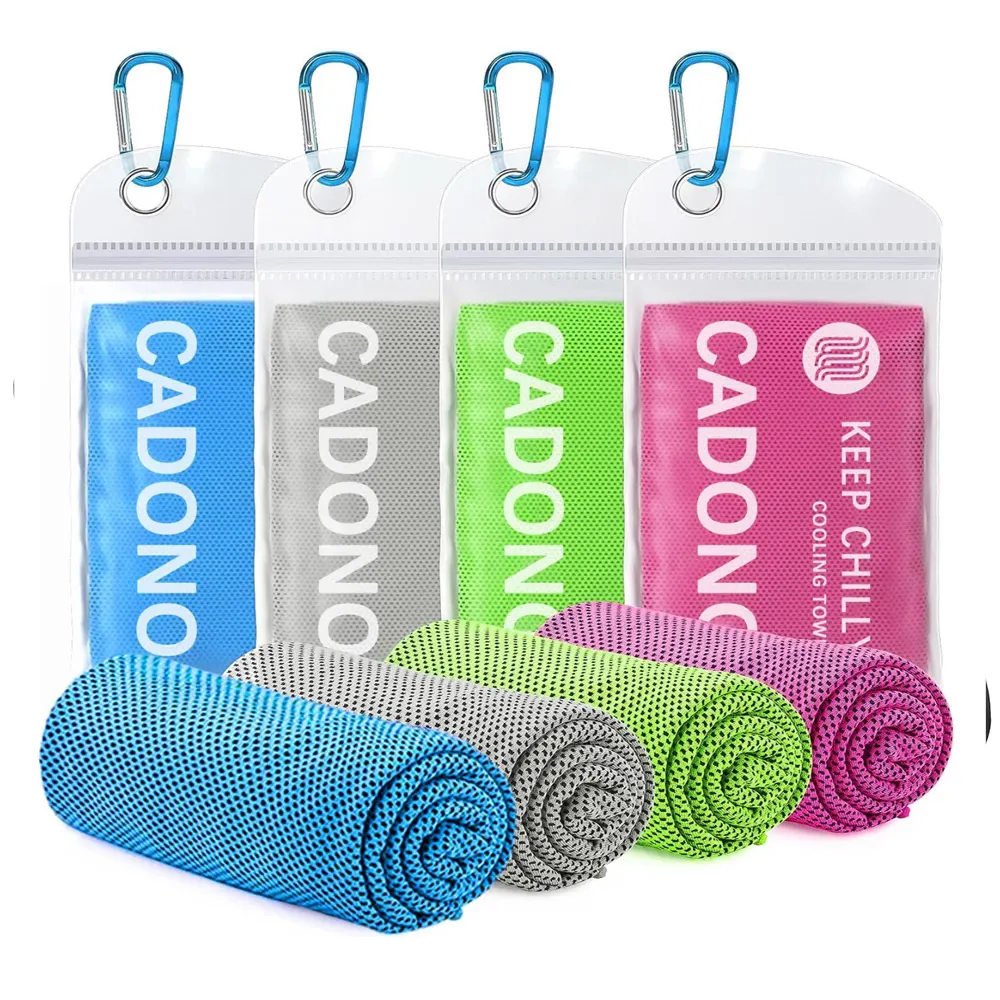
Cooling Towels
Cooling towels are an effective tool for managing heat exhaustion and heat stroke. When soaked in water and applied to the skin, they provide immediate cooling relief. These towels work by evaporative cooling, drawing heat away from the body. They are particularly useful for reducing body temperature in cases of heat stroke, where rapid cooling is necessary.
Water Purification Tablets
Water purification tablets are essential in situations where access to clean drinking water is limited. Dehydration can exacerbate heat-related illnesses, making it vital to have a safe water supply. These tablets purify water by killing pathogens, ensuring that it’s safe to drink. Staying hydrated is key in preventing and treating heat exhaustion and dehydration.
Insect Bites and Stings
Insect bites and stings can range from mild irritations to severe allergic reactions. Immediate treatment is important to alleviate discomfort and prevent more serious complications, especially in individuals with known allergies.
Antihistamines
Antihistamines are effective in reducing the symptoms of insect bites and stings, such as itching, swelling, and redness. They work by blocking the action of histamine, a substance in the body that is released during an allergic reaction. Antihistamines can be taken orally or applied topically, depending on the severity and type of reaction.
Hydrocortisone Cream
Hydrocortisone cream is a topical medication used to soothe skin irritation caused by insect bites and stings. It reduces inflammation, itching, and redness. Apply a small amount of the cream to the affected area, being careful not to use it on broken skin or open wounds. It’s particularly useful for relieving discomfort from bites that cause minor allergic reactions.
EpiPen
An EpiPen (epinephrine auto-injector) is a life-saving device for individuals with severe allergies to insect stings or bites. It delivers a dose of epinephrine, which can quickly reverse the symptoms of anaphylaxis, a severe allergic reaction that can be life-threatening. It’s crucial for individuals with known severe allergies to carry an EpiPen and know how to use it in case of an emergency.
Poisonous Plant Exposure
Exposure to poisonous plants like poison ivy, poison oak, or poison sumac can cause uncomfortable and sometimes severe skin reactions. Recognizing and treating these exposures promptly can alleviate symptoms and prevent further skin irritation.
Calamine Lotion
Calamine lotion is a topical treatment known for its soothing effect on skin irritations caused by poisonous plants. It provides relief from itching and helps to dry out the rash. The lotion creates a cooling sensation when applied, which can be comforting on the inflamed and irritated skin. It’s a go-to remedy for mild to moderate reactions and can be applied directly to the affected areas.
Hydrocortisone Cream
Hydrocortisone cream is effective in reducing inflammation and itching associated with plant-induced skin reactions. It’s a mild steroid that works by decreasing the body’s immune response to the irritants in the plant oils. Apply the cream to the rash as directed, being cautious not to use it on broken or infected skin.
Antihistamines
Antihistamines can be used to relieve systemic allergic reactions caused by exposure to poisonous plants. They work by blocking histamine, a substance in the body that causes allergy symptoms like itching and swelling. Antihistamines can be taken orally to provide relief from widespread symptoms and are particularly useful if the reaction is not localized to one area of the skin.
Infections and Sepsis
Infections, if left untreated, can escalate into sepsis, a potentially life-threatening condition caused by the body’s response to an infection. Prompt and appropriate treatment is essential to prevent the spread of infection and the onset of sepsis.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics are vitally important in treating bacterial infections. They work by killing bacteria or stopping their growth. For effective treatment, it’s important to use antibiotics specifically prescribed for the type of infection and to complete the entire course of medication as directed, even if symptoms improve.
Antiseptic Wipes
Antiseptic wipes are used for cleaning and disinfecting wounds or the skin around a wound. They help prevent infections by eliminating bacteria and other pathogens from the skin’s surface. These wipes are particularly useful in a first aid situation where immediate cleaning of a wound is necessary to reduce the risk of infection.
Sterile Dressings
Sterile dressings are essential for covering and protecting wounds from external contaminants. They provide a barrier against bacteria and help maintain a clean environment around the wound. Using sterile dressings is vital for preventing infections, especially in open wounds or after surgical procedures. Regularly changing dressings and monitoring for signs of infection are key aspects of wound care.
Gastrointestinal Issues (Diarrhea, Vomiting)
Gastrointestinal issues like diarrhea and vomiting can lead to dehydration and electrolyte imbalances, requiring prompt treatment to restore fluid balance and alleviate symptoms.
Anti-diarrheal Medication
Anti-diarrheal medications are used to reduce the frequency and urgency of diarrhea. They work by slowing down the movement of the gut, allowing more water to be absorbed from the bowel contents. This can provide quick relief from diarrhea, but it’s important to use these medications as directed and to be aware that they are not suitable for all types of diarrhea, especially if caused by certain infections.
Oral Rehydration Salts
Oral rehydration salts (ORS) are a mixture of salts that are dissolved in water. They are designed to quickly replenish fluids and electrolytes lost during episodes of diarrhea and vomiting. ORS solutions are particularly effective in preventing and treating dehydration, which can be a serious complication of gastrointestinal issues.
Anti-nausea Medication
Anti-nausea medications help to control nausea and vomiting, providing relief from discomfort and preventing further dehydration. These medications work by blocking the signals to the brain that trigger the reflex to vomit. They can be especially useful in managing symptoms of gastrointestinal infections, food poisoning, or other conditions that cause nausea and vomiting.
Respiratory Issues (Asthma, Pneumonia)
Respiratory issues like asthma and pneumonia require careful management to ensure adequate breathing and to alleviate associated symptoms. These conditions can range from chronic (like asthma) to acute (like pneumonia), and each has specific treatment needs.
Inhalers
Inhalers are a mainstay of treatment for asthma, delivering medication directly to the lungs to relieve symptoms like wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath. There are different types of inhalers, including bronchodilators that quickly open airways and corticosteroids that reduce inflammation in the airways. It’s a good idea for asthma sufferers to carry their prescribed inhaler and know how to use it correctly.
Cough Suppressants
Cough suppressants, or antitussives, are used to control coughing, a common symptom of respiratory issues like pneumonia. They work by suppressing the cough reflex in the brain, providing relief from persistent, dry coughs. However, it’s important to use them judiciously, as coughing can also be a protective mechanism to clear the airways.
Fever Reducers
Fever reducers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, are used to lower body temperature and alleviate discomfort associated with fever, a common symptom in respiratory infections like pneumonia. They also help in reducing body aches and pains. It’s important to use these medications as directed and be mindful of their interactions with other medications.
Cardiac Issues (Heart Attack)
Cardiac issues, particularly heart attacks, are critical medical emergencies that require immediate intervention. Quick response with the right supplies can be life-saving in these situations.
Aspirin
Aspirin is a key first aid item for heart attacks. It works by inhibiting platelets, which are blood cells that clot and can block coronary arteries during a heart attack. Chewing a low-dose aspirin at the onset of heart attack symptoms can help reduce the severity of the attack. It’s important to call emergency services first before administering aspirin, as they can provide guidance on the appropriate action.
Nitroglycerin
Nitroglycerin is commonly prescribed to individuals with known heart conditions. It helps in dilating blood vessels, which can alleviate chest pain (angina) associated with a heart attack. If a person has a prescribed nitroglycerin, it should be administered as directed during a cardiac event. However, it’s a wise idea not to use it if the person has not been prescribed this medication, as it can have serious side effects.
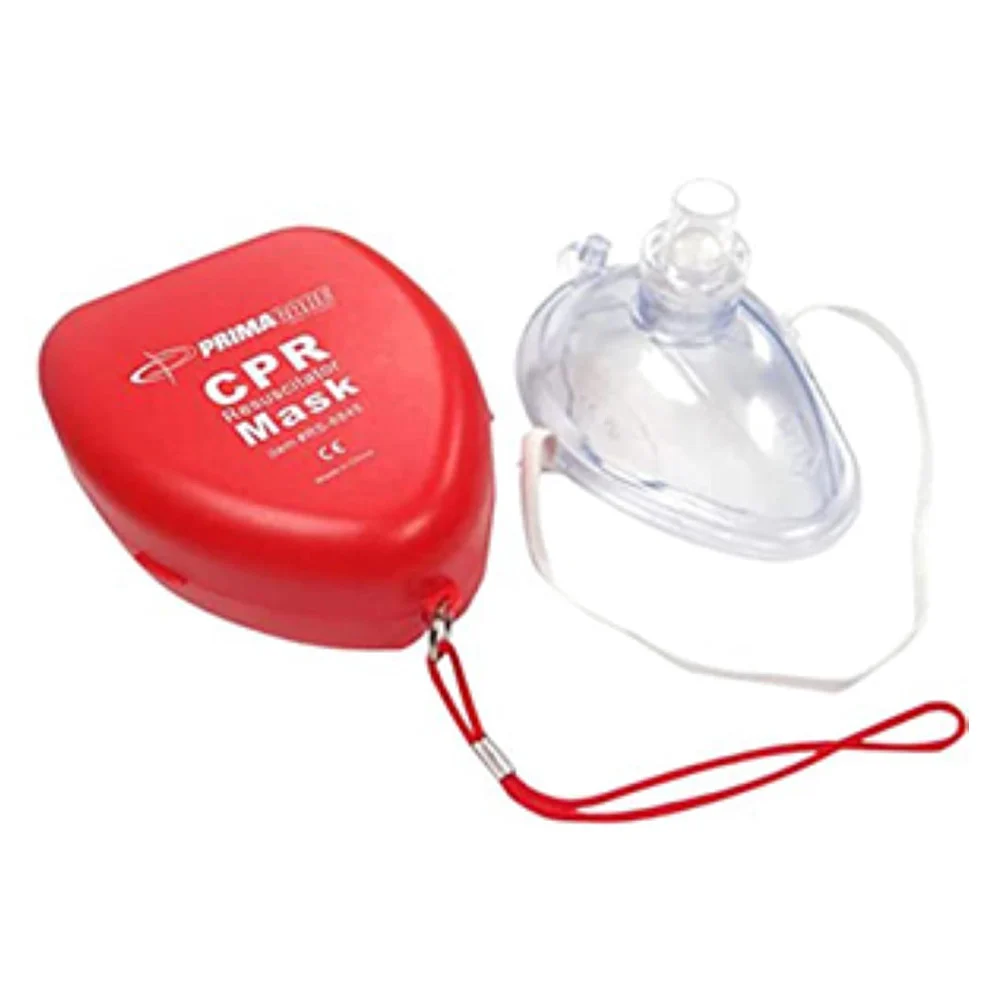
CPR Mouth Barrier
A CPR mouth barrier is a safety device used during cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR). It helps protect the rescuer from direct contact with the patient’s mouth and bodily fluids, reducing the risk of transmitting infections. The barrier typically includes a one-way valve, ensuring air only travels from the rescuer to the patient. Having a CPR mouth barrier in a medical kit is essential for safely performing rescue breathing and chest compressions on someone experiencing a heart attack.
Eye Injuries
Eye injuries can range from minor irritations to severe trauma and require immediate and appropriate care to prevent further damage and promote healing.
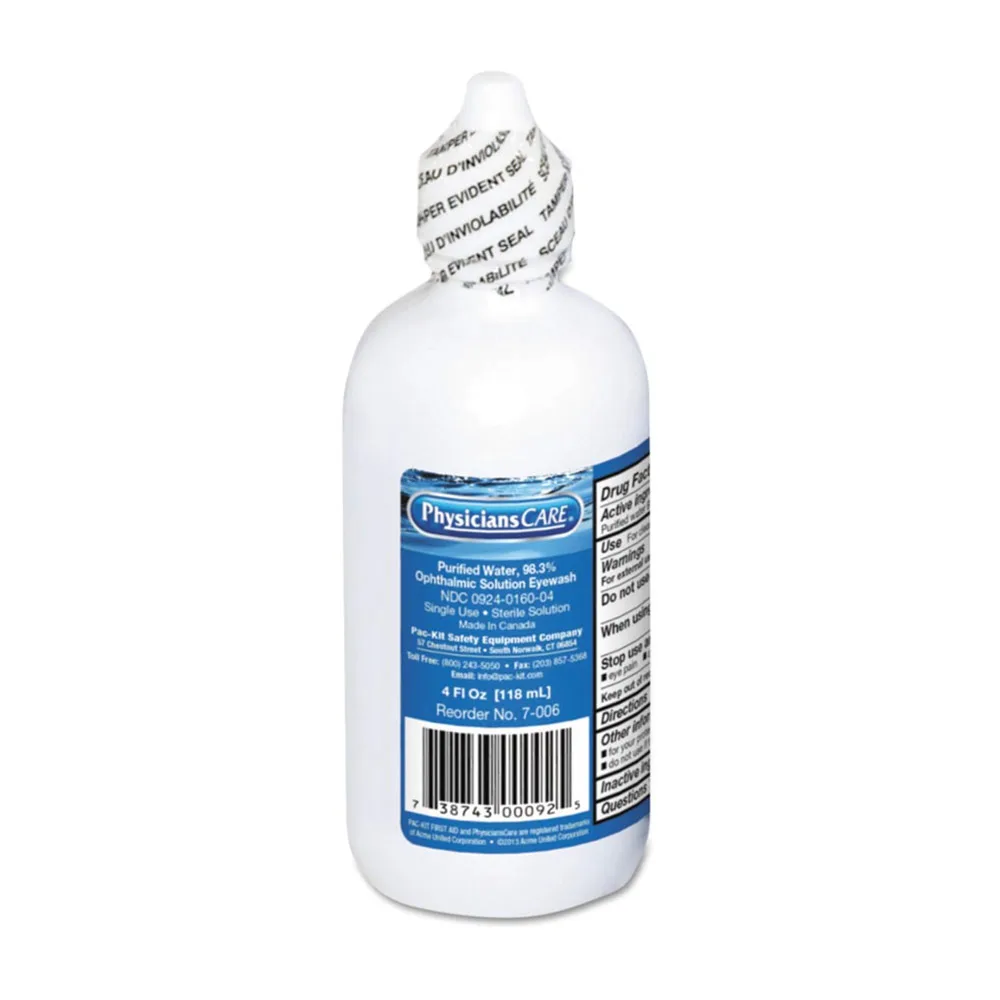
Sterile Eye Wash
Sterile eye wash is essential for flushing out foreign substances from the eye. It helps in removing irritants like dust, debris, or chemicals, providing relief and preventing further irritation or infection. In case of an eye injury, use the eye wash to gently rinse the eye, following the instructions on the package for proper usage.
Eye Pads
Eye pads are used to protect and cover an injured eye. They provide a shield against light and prevent further irritation from external elements. After administering first aid, such as flushing the eye with a sterile wash, an eye pad can be gently placed over the injured eye and secured with bandages to keep it in place.
Bandages
Bandages are used to secure eye pads in place after treating an eye injury. They should be applied carefully to avoid putting pressure on the injured eye. The bandage should be firm enough to hold the eye pad in place but not so tight that it causes discomfort or pressure.
Boric Acid Solution
Boric acid solution is sometimes used as a mild antiseptic for eye cleansing and irrigation. It can help soothe minor eye irritations and cleanse the eye, but it should be used with caution.
See: Long-Lasting Chemicals for Emergency Preparedness & Home Supply
Dental Emergencies
Dental emergencies, such as a broken tooth, lost filling, or severe toothache, require prompt care to alleviate pain and prevent further complications.
Dental Repair Kit
A dental repair kit is a valuable tool for addressing minor dental emergencies. These kits typically include temporary filling material, dental wax, or cement that can be used to cover or fill a broken tooth, lost filling, or crown. They provide a temporary solution to protect the tooth and reduce discomfort until professional dental care can be obtained.
Pain Relievers
Pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, are important for managing pain associated with dental emergencies. They can help alleviate discomfort from toothaches, swollen gums, or injuries to the mouth. It’s important to use these medications as directed and be aware of any allergies or interactions with other medications.
Gauze
Gauze is useful for controlling bleeding in dental emergencies, such as after a tooth extraction or if there’s injury to the gums or inner cheeks. It can be placed directly on the bleeding site and bitten down gently to apply pressure and stem the bleeding. Gauze can also be used to clean around the affected area gently, helping to keep it clean until professional dental care is received.
Allergic Reactions
Allergic reactions can range from mild symptoms like rashes and itching to severe, life-threatening conditions like anaphylaxis. Quick and appropriate treatment is crucial to manage these reactions effectively.
Antihistamines
Antihistamines are essential for treating mild to moderate allergic reactions. They work by blocking histamine, a chemical released by the body during an allergic reaction that causes symptoms like itching, swelling, and hives. Antihistamines can be taken orally or applied topically, depending on the type and severity of the reaction.
EpiPen (Epinephrine Auto-Injector)
An EpiPen is a life-saving device used in the treatment of severe allergic reactions, such as anaphylaxis. It delivers a dose of epinephrine, which can quickly reverse the symptoms of a severe allergic reaction, including throat swelling, difficulty breathing, and a significant drop in blood pressure. It’s important for individuals with known severe allergies to carry an EpiPen and be familiar with its usage.
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids can be used to treat severe or persistent allergic reactions. They reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system’s response. Corticosteroids can be administered orally or topically, depending on the nature of the allergic reaction. They are particularly effective in managing reactions that involve significant swelling or inflammation, such as severe cases of poison ivy or allergic asthma.
Hypoglycemia or Diabetic Emergencies
Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and diabetic emergencies are critical conditions that require immediate attention, especially for individuals with diabetes. Proper management is key to quickly restoring blood sugar levels to a safe range.
Glucose Tablets
Glucose tablets are a fast and effective way to increase blood sugar levels during a hypoglycemic episode. They are specifically designed to provide a rapid increase in blood glucose, making them ideal for emergency situations. Glucose tablets are easy to dose and consume, and they act quickly, which is crucial during a hypoglycemic event.
Sugary Snacks
Sugary snacks, such as candy, fruit juice, or honey, can also be used to quickly raise blood sugar levels in a hypoglycemic emergency. They provide a quick source of glucose that the body can rapidly absorb. It’s important to follow up with a longer-acting carbohydrate after the initial treatment to stabilize blood sugar levels.
Insulin (for Diabetics)
For diabetics, insulin may be a critical component of managing blood sugar levels. In some diabetic emergencies, such as hyperglycemia (high blood sugar), administering insulin is necessary to reduce blood sugar levels. However, insulin should only be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional and according to a diabetic patient’s prescribed insulin regimen. Incorrect use of insulin can lead to dangerously low blood sugar levels.

Pin it